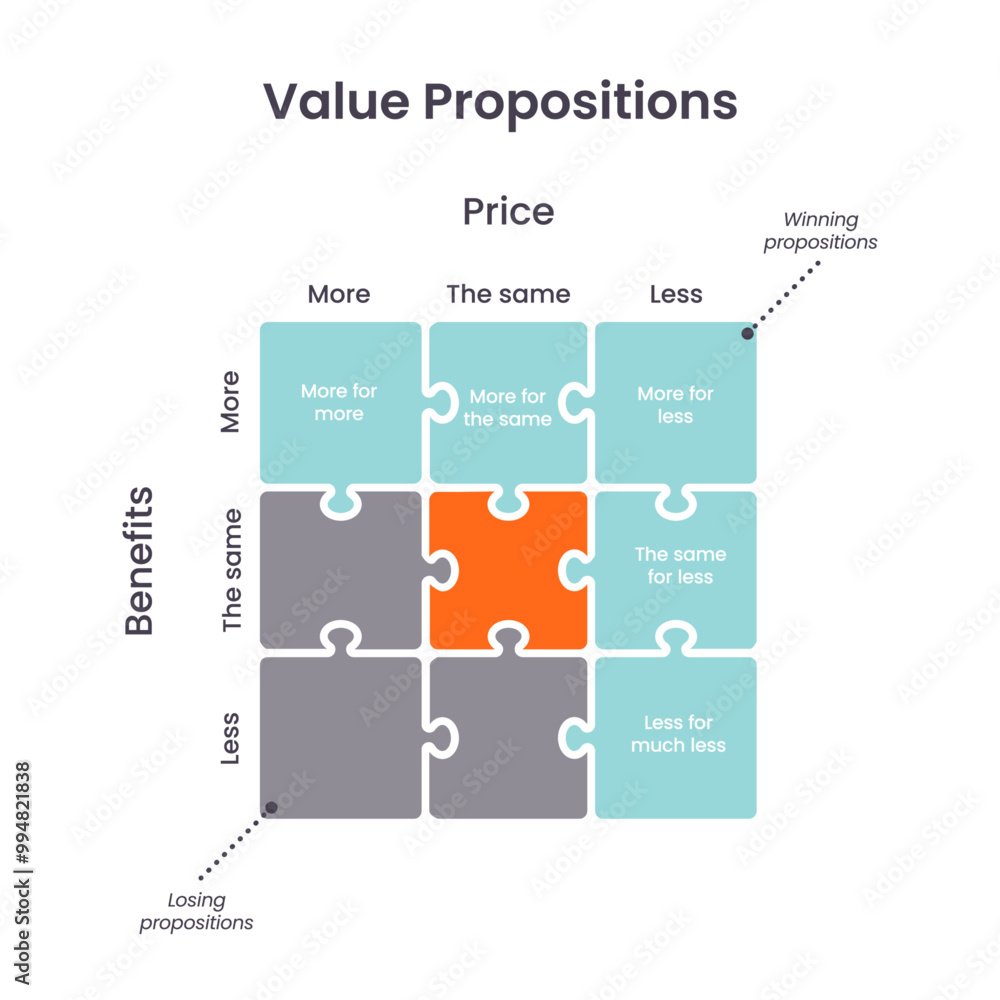
Crafting the perfect price for your product or service isn't just about covering costs; it's a strategic superpower that dictates market positioning, customer perception, and ultimately, your bottom line. Get your Pricing, Model Variations & Value Proposition right, and you unlock sustainable growth. Miss the mark, and even the most innovative offering can flounder. This isn't just accounting; it's the art and science of market success.
At a Glance: Key Takeaways for Smart Pricing
- Pricing models are frameworks, not just numbers. They use data to find the sweet spot between profit and market acceptance.
- Models vs. Strategies: Models are the how (the math); strategies are the why (the objective).
- Many flavors of pricing exist: From cost-plus to value-based, subscription, dynamic, and more—each suits different business contexts.
- Your choice isn't static: It evolves with your business, market, and customer needs.
- Optimization is ongoing: Regular studies on customer expectations and competitor moves are crucial for sustained success.
- Research is paramount: Understand your costs, your customers, and your competitors before settling on a model.
- Hybrid models offer flexibility: Don't be afraid to combine approaches to match complex offerings.
Beyond the Price Tag: What is a Pricing Model, Really?
Imagine building a house. A pricing model isn't just the final sticker price; it's the architectural blueprint that dictates how that price is constructed. It's an analytical framework businesses use to figure out the optimal selling price for their offerings. This isn't guesswork; it’s a comprehensive exploration informed by data points, market trends, customer insights, and your product's unique value proposition. The goal? To find that delicate balance between maximizing profitability and earning a positive, enthusiastic market response.
Think of it this way: A pricing model is the mathematical framework or algorithm that calculates a price based on inputs like your operational costs, the perceived value your customer places on what you offer, and how your competitors are pricing similar items. It’s a tactical tool designed to ensure you remain competitive and your business stays sustainable.
A pricing strategy, on the other hand, is the overarching philosophical approach. It’s the "why" behind the price. Are you aiming for market domination, positioning yourself as a luxury brand, or focusing on offering unbeatable value? Your strategy aligns with your company's broader objectives, rooted in extensive market research, your brand's identity, and your long-term vision. The model serves the strategy.
Unpacking the Toolkit: A Deep Dive into Pricing Model Variations
The world of pricing offers a rich palette of models, each suited to different products, services, and market conditions. Understanding these variations is the first step toward finding your perfect fit.
1. The Foundation: Cost-Plus Pricing Model (Markup Pricing)
This is perhaps the most straightforward model. You simply compute your total production or acquisition cost for a product and then add a predetermined markup percentage for your profit.
How it works: If your gadget costs $10 to produce, and you want a 20% margin, you sell it for $12.
Best for: Businesses with clear, measurable costs, often in retail for consumer goods where margins are relatively consistent. Think large chains like Target, where predictable pricing helps manage vast inventories.
2. The Customer's Lens: Value-Based Pricing Model
Instead of looking inward at your costs, value-based pricing looks outward at your customer. It focuses on the perceived value a product offers its customers, rather than just the production costs.
How it works: A piece of software that streamlines a complex business process, saving a company thousands of hours annually, can command a much higher price than its development cost because its value is immense.
Best for: High-margin, differentiated markets like enterprise software, luxury goods, or unique professional services where your offering solves a critical problem or delivers a unique experience.
3. Time as a Measure: Hourly Pricing Model
Straightforward and widely used in service-based industries, this model bills clients based on the number of hours dedicated to a project or task.
How it works: A consulting firm like McKinsey & Company, for instance, often charges clients based on the hourly rates of its consultants for strategic advisory projects.
Best for: Consultants, freelancers, agencies, and professional services where effort is directly correlated with time spent.
4. Set in Stone: Fixed Pricing Model
With this model, a product or service commands a consistent price, irrespective of the time or resources expended on any single transaction.
How it works: When you buy a gallon of milk at Walmart, the price is fixed, regardless of how long it took the store to stock it or how many customers buy it.
Best for: Standardized products, off-the-shelf software, or clearly defined service packages where scope creep is minimal.
5. Investing in Potential: Equity Pricing Model
Less common for direct product sales, this model is prevalent in the startup ecosystem. Instead of monetary payments, businesses accept equity or shares in a company as compensation, banking on future growth.
How it works: Startup accelerators like Y Combinator might provide seed funding and mentorship in exchange for a percentage of the startup's equity.
Best for: Venture capital, startup incubators, or service providers willing to take a calculated risk on a promising early-stage company.
6. Pay for Results: Performance-Based Pricing Model
This model ties charges directly to achieved outcomes or results. If the agreed-upon goal isn't met, the payment might be reduced or withheld.
How it works: A digital marketing agency might charge a base fee plus a percentage based on the number of qualified leads generated or conversions achieved for a client. HubSpot partner agencies often leverage this model.
Best for: Marketing agencies, sales consultants, or any service where measurable results are clearly defined and impactful.
7. The Ongoing Relationship: Retainer Pricing Model
Clients pay a recurring fee (monthly or annually) for uninterrupted access to a set of services or a dedicated amount of work.
How it works: Public relations firms like Edelman often operate on retainer agreements, providing ongoing media relations, crisis management, and strategic communications for their clients.
Best for: PR firms, legal services, ongoing consultancy, or any service requiring continuous support and availability.
8. Access Over Ownership: Subscription-Based Pricing
A hugely popular model, customers pay a recurring fee (monthly, quarterly, annually) for access to a product, service, or content.
How it works: Think of streaming services, software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms, or financial planning services. It lowers the initial entry cost for the customer and creates predictable recurring revenue for the business.
Best for: SaaS companies, media organizations, fitness apps, or any offering that benefits from continuous engagement and recurring value delivery.
9. Use What You Pay For: Usage-Based Pricing
Customers pay according to how much they actually use a product or service. This model directly aligns cost with consumption.
How it works: Pay-as-you-go telephone plans charge per minute or text. Cloud computing services like AWS charge based on data storage, transactions, or compute time.
Best for: Utilities, cloud services, telecommunications, or any service where consumption can be easily metered and scaled.
10. Real-Time Responsiveness: Dynamic Pricing (Surge/Demand Pricing)
This model allows prices to be flexible and adjusted in real-time based on changing market demands, supply, time of day, or other factors.
How it works: Rideshare companies famously raise prices during rush hour or periods of high demand to balance supply and demand. Airlines and hotels also extensively use dynamic pricing.
Best for: Airlines, hotels, rideshare services, event ticketing, or e-commerce platforms with fluctuating inventory and demand.
11. The Perception Play: Price Anchoring (High-Low Pricing)
This psychological pricing tactic establishes a high initial price (the "anchor") before offering a discounted price. The high anchor influences the customer's perceived value of the subsequent, lower price.
How it works: A laptop initially listed at $300, then "marked down" to $200, makes the $200 price seem like a much better deal.
Best for: Retail, e-commerce, and promotions, particularly when launching a new product or clearing inventory. This is how many deals are presented, helping customers feel like they're getting a significant saving. Should you buy iPhone 16?, for example, you might see discussions around its initial price acting as an anchor for future models or bundles.
Beyond the Model: Why the Right Choice Defines Your Future
Choosing a pricing model isn't a trivial decision; it's a strategic maneuver that directly links your business objectives, your product's perceived value, and the dynamics of your target market.
Secure Your Financial Future
At its core, the right pricing model ensures your costs are covered, healthy profit margins are maintained, and your overall financial health is secured. Incorrect pricing can lead to losses, even with high sales volumes, or stifle demand if prices are too high for the perceived value.
Build Trust and Loyalty
Fair and transparent pricing resonates deeply with customers. When they feel they're getting good value for their money, it fosters satisfaction, trust, and loyalty. This isn't just about a single transaction; it's about cultivating repeat purchases and turning customers into advocates.
Master the Market
A well-chosen model helps you position yourself effectively against competitors. It allows you to enter new markets, differentiate your offering, or even disrupt existing paradigms.
The Power of Insight: Why Price Optimization Matters
To truly nail your pricing, you can't set it and forget it. Running a dedicated price optimization study is like giving your pricing strategy a regular health check-up.
- Understand Customer Expectations: What price points are your customers truly comfortable with? What value do they perceive, and what are they willing to pay? Optimization studies reveal these crucial insights.
- Decipher the Competitive Landscape: Get a clear overview of your competitors' pricing structures. This identifies gaps, potential differentiators, and areas where you might be leaving money on the table or losing customers unnecessarily.
- Ensure Accurate Existing Product Pricing: Markets evolve, costs change, and customer perceptions shift. Optimization helps you recalibrate prices for existing products to align with current dynamics, preventing stagnation or missed opportunities.
- Fuel Customer Retention: By delivering consistent, perceived value at the right price, you foster loyalty and contribute directly to sustained customer retention and growth.
Crafting Your Pricing Blueprint: A Step-by-Step Guide
So, how do you navigate this complex landscape and choose the model that's right for your business? It’s a structured process that combines internal analysis with external market understanding.
Step 1: Analyze Your Cost Structure & Evaluate Competitor Pricing
Before you can price anything, you need to know what it truly costs you.
- Internal Audit: Detail all your costs: production, marketing, sales, overhead, R&D, and even the cost of customer support. Don't forget the intangible costs of your time and resources.
- Competitor Deep Dive: Look at your direct and indirect competitors. How are they pricing similar offerings? What value are they creating? What buying signals are they sending to the market? Are their models transparent or opaque?
- Scenario Building: Based on this data, create 3-5 potential pricing scenarios. This helps you visualize different profit margins and market impacts.
Step 2: Check Your Business Capabilities for Implementation
A brilliant pricing model is useless if you can't execute it.
- Infrastructure & Technology: Do you have the systems in place to handle complex tiered pricing, usage tracking, or dynamic adjustments?
- Production & Manufacturing: Can you scale production if a lower price point drives massive demand? Or maintain exclusivity for a premium model?
- Staffing & Resources: Does your sales team understand the new model? Do you have the customer support capacity? Consider the timelines and resources required for each potential model.
Step 3: Conduct Thorough Customer Research
Your customers are the ultimate arbiters of value. You need to understand their perception and willingness to pay.
- Customer Interviews (Qualitative): Engage small groups or one-on-one with existing customers. Ask open-ended questions about their pain points, how they value your solution, and what they'd be willing to pay. This uncovers motivations and objections.
- Customer Surveys (Quantitative): Use insights from interviews to craft closed-ended questions for larger groups. This provides statistically significant data on preferred price points, feature bundling, and overall market acceptance. Tools like Van Westendorp's Price Sensitivity Meter or Gabor-Granger can be invaluable here.
Step 4: Select Your Pricing Model
Armed with comprehensive data, it's time to make an informed decision.
- Synthesize Information: Review all your findings: cost analysis, competitor insights, and, critically, customer research.
- Align with Goals: Does the model support your overarching business goals (e.g., market share, profit maximization, rapid growth)?
- Evaluate Pros & Cons: Weigh the benefits and drawbacks of each potential model on revenue, profitability, competitive advantage, and operational complexity.
- Focus on Willingness to Pay: The sweet spot is where your price aligns with your customer's perceived value and willingness to pay, while also ensuring your profitability.
Step 5: Implement and Monitor (This is Not a One-Time Fix!)
Pricing is an ongoing journey, not a destination.
- Launch Strategically: Roll out your chosen model, perhaps starting with a pilot program or A/B testing different variations.
- Continuous Monitoring: Keep a close eye on internal sales metrics, conversion rates, customer feedback, and churn.
- Market Awareness: Stay vigilant about changes in competitor pricing, new product launches, shifts in your customer base demographics, and broader economic changes. Be prepared to adapt.
Pricing in the Wild: Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries, different strokes. The ideal pricing model often varies dramatically based on the nature of the product, customer expectations, and competitive landscape.
SaaS and Software
This industry heavily favors subscription-based and tiered pricing models, often with a freemium option to attract users. The trend towards usage-based pricing is also rising, with giants like AWS charging per transaction or gigabyte. Hybrid models combining fixed recurring fees with variable usage charges are becoming common, offering flexibility and scalability.
E-commerce and Retail
Here, dynamic pricing reigns supreme. E-commerce behemoths like Amazon adjust prices millions of times daily based on demand, competition, time of day, and even individual user browsing history. Bundle pricing is also effective to boost average order value by grouping complementary products at a slightly reduced combined price.
Professional Services (Consulting, Law, Creative Agencies)
Traditionally, hourly pricing dominated. However, there's a significant shift towards fixed project rates for clearly defined scopes, and increasingly, value-based pricing as firms aim to charge for the impact they deliver rather than just the time spent. Retainer agreements are crucial for building long-term partnerships and ensuring continuous revenue. Some agencies also experiment with performance-based or hybrid models, especially in areas like marketing.
Manufacturing and B2B
Cost-plus or markup pricing are common starting points, given the often clear production costs. Volume-based discounts are essential for large orders, and contract pricing for long-term supply agreements is standard. There's a growing exploration of usage-based leasing models, where businesses pay per machine hour or output, rather than outright purchase.
Staying Ahead: Key Trends & Smart Strategies
The pricing landscape is constantly evolving. Staying informed about current trends and adopting best practices will keep you competitive and profitable.
The Rise of Recurring Revenue
A significant trend: 60% of businesses are now adopting subscription-based pricing, especially within the SaaS sector. This shift reflects a desire for predictable revenue streams and sustained customer relationships.
The Power of Choice
Firms that offer three distinct pricing tiers (e.g., basic, standard, premium) report, on average, 35% more revenue than those sticking with a flat pricing structure. Offering choices helps capture different customer segments with varying needs and budgets.
Agility is King
Dynamic pricing strategies are proving incredibly effective, increasing revenue by 12% on average by responding to real-time market fluctuations. The ability to adapt prices quickly is a powerful competitive advantage.
Value Pays Off
Focusing on the perceived benefits to the customer rather than just internal costs, value-based pricing achieves 18% higher profit margins. When you can clearly articulate and demonstrate the value you provide, customers are willing to pay more.
Don't Guess, Test!
A/B testing different pricing models or variations can yield a 14–17% increase in profits. This highlights the importance of data-driven experimentation over intuition.
Essential Tips and Best Practices
- Establish a Pricing Point Person/Team: Pricing shouldn't be an afterthought or a once-a-year review. Designate someone or a small team to continuously monitor, analyze, and optimize your pricing strategy. It needs to be an ongoing process.
- Don’t Overcomplicate It: While internal models can be sophisticated, keep your customer-facing pricing simple, clear, and easy for your sales team to explain and for customers to understand. Confusion breeds hesitation.
- Explore Hybrid Pricing Models: For businesses with multiple products or services, or complex value propositions, combining elements from different models (e.g., a fixed retainer with performance-based bonuses) can offer the best of both worlds – flexibility and diversified revenue streams.
- Test Pricing Model Options Relentlessly: Whether it's through A/B testing on your website, small pilot programs, or trials with specific customer segments, actively test and gather data on how different pricing approaches perform before a full rollout.
Your Pricing Playbook: Moving Forward with Confidence
Pricing isn't a static number you assign and forget; it's a dynamic lever that, when pulled correctly, can accelerate your business growth and solidify your market position. By understanding the various pricing models, aligning them with your strategic goals, deeply understanding your customers, and committing to continuous optimization, you transform pricing from a cost center into a core driver of value.
Take the insights you've gained here and start asking the critical questions about your own business: What value do you truly deliver? What are your customers willing to pay for that value? And how can your pricing model best communicate that proposition? The answers will not only define your immediate success but also chart the course for your long-term market leadership.